Table of Contents
What is Uveitis?
Meaning of Uveitis:
Uveitis (Pronounced “yoo-vai-tuhs”) is a condition that causes inflammation in your eye. It affects the middle layer of the eye i.e., the Uvea.
It can affect either one or multiple areas of the eye and depending on where it affects, it can be painful, irritating, and in certain cases, it may even destroy your vision. This condition can affect one or both eyes of people of all ages, including children.
The causes of uveitis are usually hard to identify, however, some possible causes could be an infection, eye injury, or autoimmune diseases.
If not diagnosed and treated at the earliest, uveitis can cause permanent blindness. Are you experiencing the symptoms of eye inflammation? If yes, then it is advisable to seek treatment from your eye specialist as soon as possible to prevent severe eye damage.
Symptoms and Causes of Uveitis:
Symptoms of Uveitis:
Usually, the uveitis symptoms occur suddenly, but in some cases, they may even develop slowly and gradually.
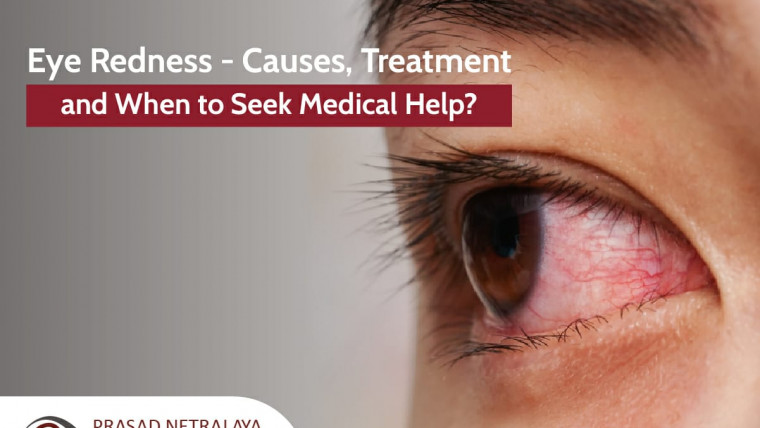
The signs and symptoms of Uveitis are as follows:
- Eye pain
- Eye redness
- Sensitivity to light (Also known as Photophobia)
- Blurred or Cloudy Vision
- Floaters (These are floating spots in the eyes that look like small transparent threads or lines moving freely in the field of vision)
- Headaches
- Reduced vision
The above symptoms may affect one or both eyes. In rare cases, these uveitis symptoms may not be detected in the eye exam.
Causes of Uveitis:
Uveitis can happen in anyone, no matter what age group one belongs to. The specific uveitis causes are usually unclear, but one of the most common reasons for the inflammation of the eye is autoimmune diseases.
Some of the possible causes are as follows:
1. Autoimmune or inflammatory disorder:
This happens when a healthy immune system tries to fight against diseases or infections and ends up accidentally attacking healthy tissues or organs.
Some of the most common autoimmune or inflammatory disorders that cause uveitis are as follows:
- Psoriasis
- Crohn’s disease
- Arthritis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis (Uveitis is a common complication among those who suffer from this type of inflammatory disease)
2. Eye injury or surgery
3. Side effects of medications
4. Infections: Infections are also possible causes of Uveitis eye. Some of the infections that increase the risk of Uveitis are as follows:
- HIV or AIDS
- Cat-scratch disease
- Herpes simplex
- Tuberculosis
- Lyme disease
- Syphilis
- Toxoplasmosis
5. In rare cases, Lymphoma (a type of cancer) may cause uveitis
Types of Uveitis
The type of Uveitis you have can vary depending on which part of your eye is inflamed.
The four major types of uveitis are as follows:
- Anterior Uveitis: It affects the front inside part of your eye, i.e., between the cornea (the clear front surface of your eye), the iris (the colored part of your eyes), and the ciliary body. This is also called IRITIS and it is the most common type.
- Intermediate Uveitis: It affects the retina and the blood vessel located just behind the iris (pars plana) and also the gel layer in the middle of the eye (vitreous)
- Posterior Uveitis: It affects the back inside part of your eye i.e., either the retina or choroid (the layer behind)
- Panuveitis: When all the layers of the uvea are inflamed, from the front to the back, it’s called Panuveitis
When should you consult a medical specialist:
If you are experiencing any of the above warning signs of uveitis, make sure to contact a doctor immediately. They may refer you to an eye specialist if your problem needs attention. Make it a point to get your eyes checked at the earliest, if the pain is severe or if you’re experiencing an unexpected vision problem.
Request an appointment to seek immediate medical attention.
Treatment of Uveitis:
A person with uveitis should receive immediate and appropriate treatment, because if they don’t, then the chances of recovering are difficult.
If not treated, the person may be exposed to risks of cataracts, retinal edema, or permanent blindness.
1. Anterior Uveitis Treatment:
For this type of uveitis:
- The doctors may recommend taking eye drops that dilate pupils to avoid muscle spasms in the iris and the ciliary body
- Or they may recommend taking eye drops that contain steroids, like prednisone, to reduce inflammation
2. Interior, Posterior, and Panuveitis Treatments:
For these kinds of Uveitis, the treatments may include injections around the eye, oral medications, or surgical implants. Before proceeding with these treatments, the doctors will ensure there’s no infection in sight.
3. Treatment of uveitis from infections:
If uveitis arises from infections, doctors may prescribe antibiotics and medications combined with corticosteroids to fight the root cause.
The speed of your recovery entirely depends on the part of your eye that is infected, the kind of uveitis, and the severity of the symptoms.
4. Treatment of uveitis from autoimmune disorder:
If an ophthalmologist notices that there’s an autoimmune disorder, they will advise you to visit a rheumatologist.
Also Read : How To Treat Symptoms of Uveitis: Everything You Need To Know
Contact your nearest trusted eye specialist
Your eye health and vision are as important to us as it is to you. For expert care in managing uveitis and protecting your eyesight, consider contacting specialists at Prasad Netralaya Eye Hospital.
Schedule an appointment today and receive the best eye treatment from specialists in this field.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
1. What is the main cause of uveitis?
Uveitis is inflammation inside your eye which is usually caused when your immune system is fighting an infection and accidentally attacks a healthy tissue in your eye.
2. What food helps reduce uveitis?
Green leafy vegetables, blueberries, tomatoes, and cherries may help reduce uveitis. Supplements that contain vitamins A, C, E, and B are also recommended. There is no proven food which will help reduce uveitis
3. What is the best treatment for uveitis?
Doctors may initially prescribe eye drops having anti-inflammatory medication such as corticosteroids. However, you will require other forms of treatment if the inflammation is beyond the front of the eye.
4. Can my vision come back after uveitis?
Modern treatments help retain your vision and prevent blindness if treated early. However, recovery depends on the kind of uveitis you have.
Dr. Vikram Jain, M.S. had his medical training (MBBS) from Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, India. He did his master’s in Ophthalmic surgery from Kasturba Medical College, Manipal. He currently manages the Glaucoma department of Prasad Netralaya hospital.