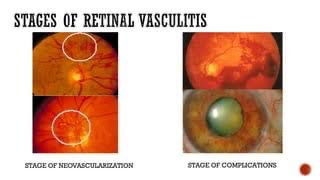
Retinal vasculitis is inflammation of retinal vessels, often due to primary eye diseases or systemic vasculitis like Behçet’s disease, sarcoidosis, or multiple sclerosis. It shows as vascular leakage and staining on fluorescein angiography, regardless of clinical signs. It can be localized to the retina or related to systemic conditions, including viral and autoimmune diseases.
What Causes Retinal Vasculitis?
There are two distinct types of causes of retinal vasculitis, namely, primary and secondary causes. This depends on whether the vessel is the primary target of the inflammatory process or a secondary one.
Primary Causes of Retinal Vasculitis
(a) Localized to the eye:
- Idiopathic
- Intermediate Uveitis of the Pars Planitis type
- Frosted Branch Angiitis
- Idiopathic Retinal Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
(b) Involves the eye and other organs:
- Giant Cell Arteritis
- Takayasu Arteritis
- Polyarteritis Nodosa
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis
Secondary Causes of Retinal Vasculitis
(a) Localized to the eye:
- Ocular Sarcoidosis
- Birdshot Chorioretinopathy Retinal Vasculitis
- Necrotic Herpetic Retinopathies (Herpes Simplex, Varicella Zoster Virus)
- Toxoplasmic Retinochoroiditis
- Tuberculosis
- DUSN (Diffuse Unilateral Subacute Neuroretinitis)
- Primary Ocular Lymphoma
(b) Associated with systemic involvement:
- Sarcoidosis
- Behçet’s Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Spondyloarthritis with HLA-Associated Uveitis
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Relapsing Polychondritis
- Tuberculosis
- Syphilis
- Lyme Disease
- Viral (Cytomegalovirus, HIV, West Nile)
- Intravenous Immunoglobulins
- Inhalation of Methamphetamine
- Cancer-Associated Retinopathy
- Oculocerebral Lymphoma
Retinal Vasculitis Diagnosis
Retinal vasculitis alone is rare. Systemic evaluation is crucial to identify potential underlying disorders. If only retinal vasculitis is present, further tests—like chest X-ray, blood tests, and biopsies—are necessary to rule out systemic diseases.
Retinal Vasculitis Symptoms
Here are some of the symptoms associated with retinal vasculitis:
- Blurry vision (painless)
- Visual floaters
- Scotomas (a dark spot in your vision)
- Decreased ability to distinguish colours
- Metamorphopsia (distortion of the shape of objects)
Retinal Vasculitis Treatment
Looking for a Consultation?
If you or anyone you know suspects the possibility of retinal vasculitis brought about by any of its accompanying causes, get an expert consultation instantly.