From watching movies to putting a thread through a needle, our eyes play a significant role in our lives. With an intricate process and design, our vision is by far one of the most phenomenal aspects of the human species.
The eye is very delicate and complex in nature. Even the smallest changes can have a big impact on our vision. And so, we need to treat it very carefully and stay alert for any changes that may occur over time. While some changes don’t have a significant impact on our lifestyle, some changes do. Retinal Detachment is one such change.
Table of Contents
What is Retinal Detachment?
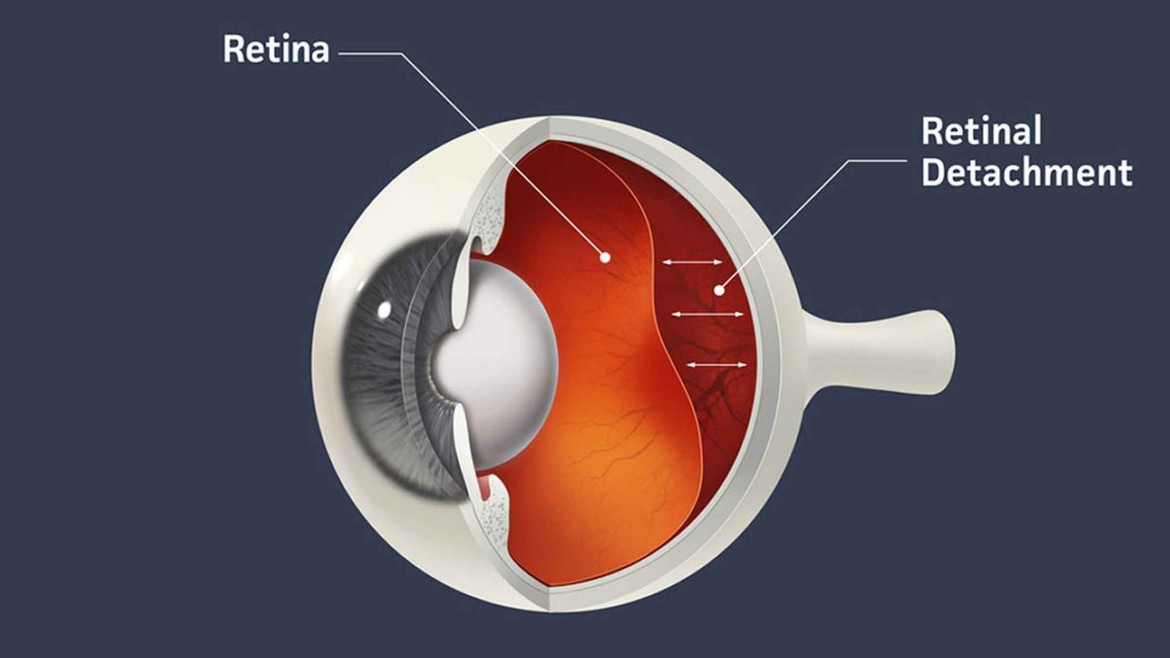
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye. The purpose of the retina is to receive light and send the signals to the brain. Retinal detachment occurs when the retina of the eye shifts its position, causing it to lose access to its circulation thus causing visual loss
Causes
Retinal detachment occurs when the layer of tissue in your eye it is no longer in its normal position and can happen for various reasons.
Some of the most common causes for your retina to become detached include small tears in the retina, a blunt force over the eye due to a fall or a hit.
Types of Retinal Detachments and their causes
Retinal detachment tends to cause visual loss as the detached retina is no longer able to perceive light adequately.
There are 3 types of retinal detachments.
-
Rhegmatogenous
Rhegmatogenous detachments are the most common type of retinal detachments. They are caused by a hole or tear in the retina that allows fluid to pass through and gather underneath the retina, pulling the retina away from underlying tissues.
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment occurs due to the vitreous, the clear gel in the middle of the eye. As we grow, the vitreous may shrink and pull on the retina. This pull on the retina can cause flashes of light or in medical terminology, photopsia. This appears as white or colored lights in the absence of any visual stimuli. The shrunken gel can also cast shadows on the retina which appear as floaters. Sometimes when the pull on the retina creates a tear there is some bleeding in the eye which appears like a shower of small black dots
-
Tractional
This type of retinal detachment occurs when new, abnormal vessels that grow on the retina’s surface, separates the retina from the back of the eye. This detachment is usually seen in people who have poorly controlled diabetes.
-
Exudative
In Exudative retinal detachment, the fluid accumulates beneath the retina, but there are no holes or tears in the retina. Exudative detachment can be caused by age-related degeneration, inflammatory disorders, etc. Unlike other forms of detachment, this is treated with medications and not surgery.
Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is quite painless, only leaving blurry spots, specks, and patches in your vision which can be easily detectable. It is advised to take immediate action when noticed. The longer your retinal detachment goes untreated, the greater the risk of permanent vision loss. So it’s very important to get it treated the minute you notice something interfering with your sight.
Early Signs of Retinal Detachment
- A sudden appearance of many specks, dots or smudges that seem to drift through your field of vision
- Bright flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
- Blurry vision
- Gradually reduced peripheral vision
- A curtain-like shadow over your field of vision
Risk Factors
The following factors increase the potential of retinal detachment in your eye:
- Age – retinal detachment tends to be more common in people over age 50
- Previous retinal detachment in one eye
- Previous eye diseases or surgeries, such as cataract removal
- Previous severe eye injury
- Heredity
- Extreme nearsightedness (myopia)
Treatment for Retinal Detachment
An ophthalmologist can determine retinal detachment through a number of painless and noninvasive tests. Surgery has proven to be a successful treatment for retinal detachment. However, the success of the surgery is dependent upon the severity of the detachment. The earlier the detection, the better the outcome. It’s also advised to notify the doctors and begin surgical procedures within 24 hours from the time of detection.
Typical surgical procedures include:
-
Laser Surgery
Repairs tears in the retina that seals the tears in the retina preventing further detachment. This is possible only when the retina is not detached or minimally detached.
-
Vitrectomy
The vitreous gel in the eye is removed and a gas bubble or silicone oil bubble is used to hold the retina in place. The tear is lasered to seal it. This can be done by minimally invasive incisions less than an mm across which heal without stitches. The silicone oil is removed within 2-8 months of post-surgery. This is the only form of treatment in tractional retinal detachments.
-
Pneumatic Retinopexy
A gas bubble is placed in the eye that places the retina back in place. Laser surgery may then be used to place the retina in the right place permanently.
-
Scleral Buckling
A silicone buckle or strap is stitched into the eye that alters the pull on the retina which allows the retina to reattach itself. However multiple sutures need to be placed in this surgery.
-
Cryopexy
The application of cold treatments to the underlying tissue, causing a scar that holds the retina in place.
Now that you know more about Retinal Detachment, don’t waste time if you detect the same in your eye or the eyes of your loved ones. Schedule an appointment immediately by calling our Toll-free number 18004251919 or our mobile number +91 9513576565. You can also learn more about the ways to prevent retinal detachment from our experts at Prasad Netralaya- Mangalore and Udupi’s first and finest Super Specialty Eye Hospital.
You can also directly book an appointment with our experienced in-house ophthalmologists by filling this simple form for regular eye checkup or just walk into any of our branches in Mangalore, Sullia, Tirathalli, and Udupi.
Dr. Vikram Jain, M.S. had his medical training (MBBS) from Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore, India. He did his master’s in Ophthalmic surgery from Kasturba Medical College, Manipal. He currently manages the Glaucoma department of Prasad Netralaya hospital.